How Is Eating In Dysphagia?
The diet in dysphagia must be adapted to the needs of each patient. In general, it is important to pay attention to the textures of foods, as there is a risk of choking. What should we know about it?
To begin with, let’s remember that normal swallowing allows all food to pass from the mouth into the esophagus. It includes the joint work of the structures of the head, neck and thorax, and the closure of the airways to avoid their obstruction.
Its characteristic is efficiency, that is, we can ingest all the food and water necessary for the body; also safety, because it protects the respiratory tract from possible complications.
What is dysphagia?
The term dysphagia comes from two Greek words: “dys” (difficulty) and “phagia” (eating). It is a sensation of difficulty in swallowing solid or liquid food and, in some occasions, it can cause pain.
Difficulty with solids indicates that there is a problem with obstruction, while dysphagia with liquids indicates a functional alteration.
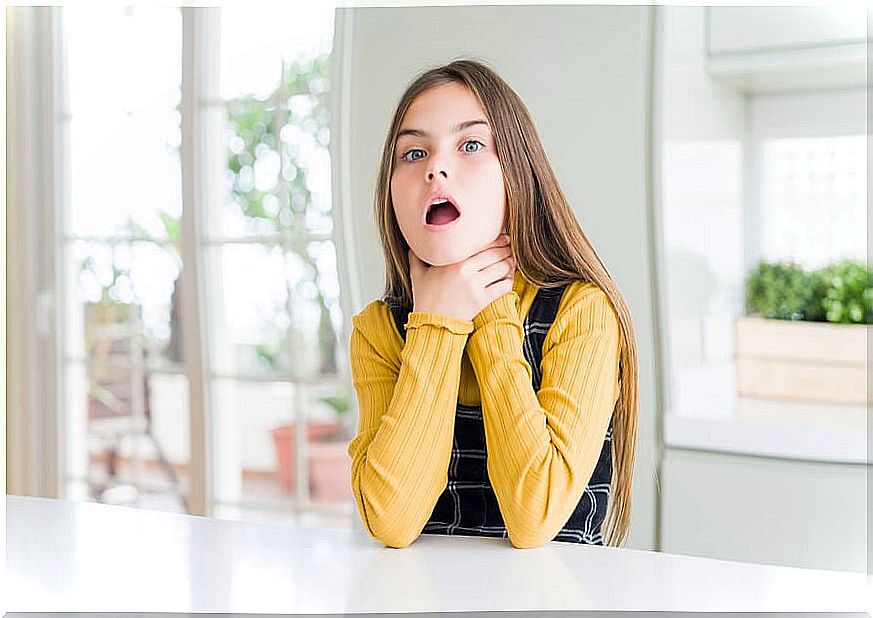

Types of dysphagia
- Upper or oropharyngeal: includes disorders of oral swallowing, pharynx and larynx, where there are problems to form or move food from the mouth to the esophagus. Sufferers may experience coughing or choking. According to a publication in the journal Nutrición Hospitalaria, almost 80% of diagnoses are of this type.
- Lower or esophageal : refers to alterations of the esophagus and produces the sensation that food sticks in the throat or chest, which causes difficulty in continuing to swallow. They represent almost 20% of diagnosed dysphagias.
What are the causes of dysphagia?
There are several factors related to the development of dysphagia. Among the most common are:
- Developmental problems.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Tumors in the head, esophagus, larynx, mouth.
- Narrowing of the esophagus.
- Neurological problems such as acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA), Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), head trauma (CET), dementia, Alzheimer’s, among others.
- Post-surgery or post-treatment of some diseases.
Now, in terms of its symptoms, it is important to bear in mind that it may cause more need to drink water with meals, dry mouth, feeling that food is sticking in the throat, frequent respiratory infections, among others.
Health consequences
The person with dysphagia does not feel safe because they are afraid of choking. Consequently, you consume less food and drink. This decrease negatively affects health, as it leads to complications such as:
- Malnutrition
- Dehydration
- Aspirations
- Pneumonia
- Respiratory infections
Feeding Considerations in Dysphagia
- Ideally, ensure a safe position, sitting with your back in contact with the back of the chair and your feet flat on the floor.
- In case of being in bed, it is advisable to maintain the 45º position, with the head forward.
- It is important not to feed anyone who is sleepy or sleepy, to avoid choking.
- Avoid distractions during the meal.
- Do not use syringes or straws.
- The environment should be comfortable and calm.
- Monitor the patient during meals.
- Maintain proper oral hygiene to reduce the risk of respiratory infections in the event of aspiration.
Although anyone can be affected by dysphagia, there is a higher risk in older people because their muscles are weaker when swallowing, which also makes them more prone to developing neurological diseases.

Diet in dysphagia
As we have already mentioned, the degree of dysphagia or food tolerance is what will determine the texture of the foods to be eaten. Liquids can be thickened with commercial products, or solids can be processed to the texture of porridge, nectar, or liquid. Even colorants can be used to improve the appearances of the dishes.
It is essential that the final textures are homogeneous, not sticky, and that they do not break easily. Another important aspect is the volumes. Similarly, if necessary, the use of nutritional supplements can be assessed, following the instructions of a professional.
For all the aforementioned, we must consider that the faster the detection of this condition, the easier it will be to prevent its advance, prevent its complications and take care of health.