What Is Scleroderma?
Scleroderma is a rare autoimmune disease. It is characterized by a thickening and hardening of the skin. It produces a build-up of scar tissue and causes organ damage. It affects, for example, the heart, lungs, kidneys and stomach. In some respects, it has similarities to lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Another curious characteristic of this disease is that it usually affects mostly middle-aged women, between 30 and 50 years old. However, it can occur in patients of any age.
Causes of scleroderma
Currently, the exact causes of scleroderma are unknown. However, the disease is known to be related to the immune system in addition to:
- Perivascular inflammatory infiltrates, which in turn are related to immune activation and the production of antibodies.
- An excessive activation of fibroblasts. They are cells responsible for synthesizing connective tissue. This causes fibrosis.
Among the factors that originate these processes, current research points to an influence of genetic inheritance. On the other hand, the environment could modify the progression of the disease. More specifically, exposure to toxic agents, oxidative stress and free radicals.
Types of scleroderma
There are different types of scleroderma with very different prognoses. However, all the different types can be classified into two large groups :
- Localized scleroderma: this type of scleroderma is characterized by affecting only the skin, without Raynaud’s phenomenon occurring. Because of this, it has a better prognosis.
- Systemic scleroderma : this type, in addition to presenting a skin condition, causes visceral damage. This is why it has a worse prognosis.

Symptoms
The symptoms of this disease vary for each person depending on the severity. Also depending on the type of scleroderma you suffer from. Some of the possible symptoms are :
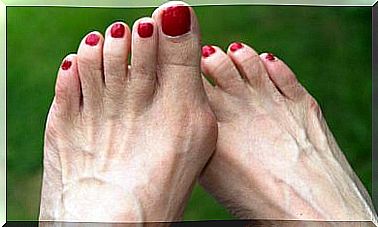
- Progressive hardening of the skin : This is the most common sign of scleroderma. For a variable number of years the affected person will show this hardening of the skin . It occurs especially in the hands (sclerodactyly). It is accompanied by the Raynaud phenomenon.
- Raynaud’s phenomenon : it is a vascular disorder characterized by a lack or reduction of blood supply in the fingers (ischemia) on an episodic basis. It manifests itself with an alteration in the color of the hands after exposure to cold and their redness when heated.
- Numbness of the fingers and toes : This sign is an exaggerated response to cold. It can cause numbness or pain. It is accompanied by the color changes in the extremities mentioned.
- Digestive system problems : gastrointestinal disorders mainly affect the esophagus. However, any part of the digestive tract can be altered.
- Lung problems : Scleroderma patients have trouble breathing. Also, in general they suffer a gradual deterioration of lung function. It is a consequence of fibrosis of the lungs. This is the main cause of death in these patients.
- Heart condition : This condition occurs rarely. It manifests itself mainly in the form of arrhythmias and anginal-type chest pain.
- Kidney malfunction : when it affects the kidney, we speak of nephropathy. It manifests itself in the first years of the disease.
Other symptoms of this disease include joint pain, hair loss, a dry cough, and wheezing (the sound that air makes as it passes through congested airways).
Diagnosis
If you suspect that you may have scleroderma, you should go to your doctor for appropriate tests. Among the tests that the doctor may ask for detecting scleroderma include:
- A blood test to detect the presence of antibodies.
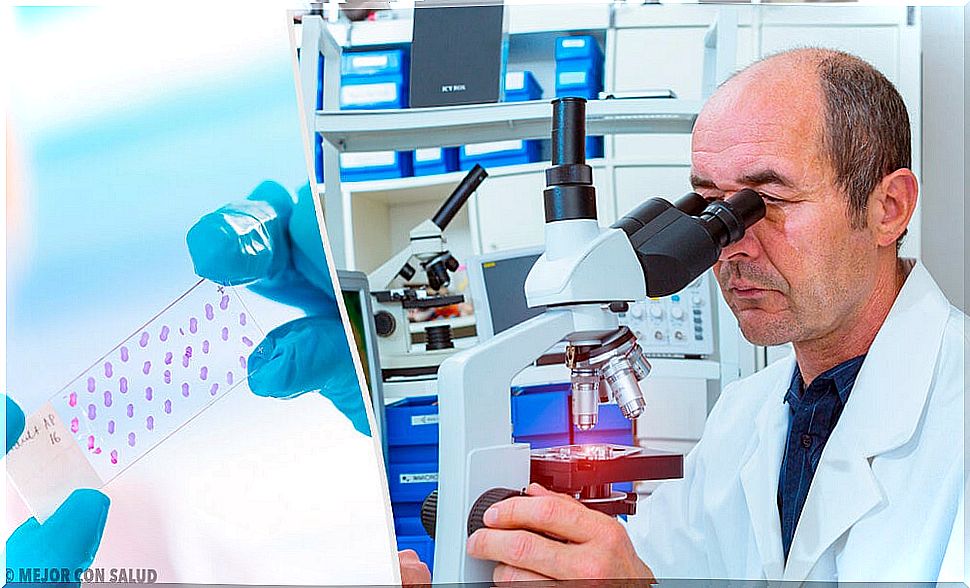
- A capillaroscopy : This test allows the microscopic vessels in the skin to be seen.
- Skin biopsy : This test consists of taking a piece of skin to analyze it under a microscope.

Scleroderma treatment
Currently, there is no allopathic treatment to cure the disease. Because it is a heterogeneous condition, treatment must be tailored to each patient.
Starting from there, there are certain symptoms that can be treated with medications. Among them are cortisone and in the most severe cases immunosuppressants. These symptomatic treatments are key to improving the prognosis of the disease.
Likewise, they can be complemented with certain non- drug care. One example is physical therapy, which helps maintain joint mobility. On the other hand, because the skin becomes fragile, it will be necessary to protect it from the cold and the sun. In addition, it is advisable to apply moisturizers.
In parallel, some simple measures can be implemented to alleviate symptoms. Some of them are:
- Give up smoking.
- Get regular physical exercise such as walking or swimming.
- Take care of your diet, in this way you will avoid being overweight.
In conclusion, as we have mentioned, the essential thing is to go to the doctor before any suspicion.