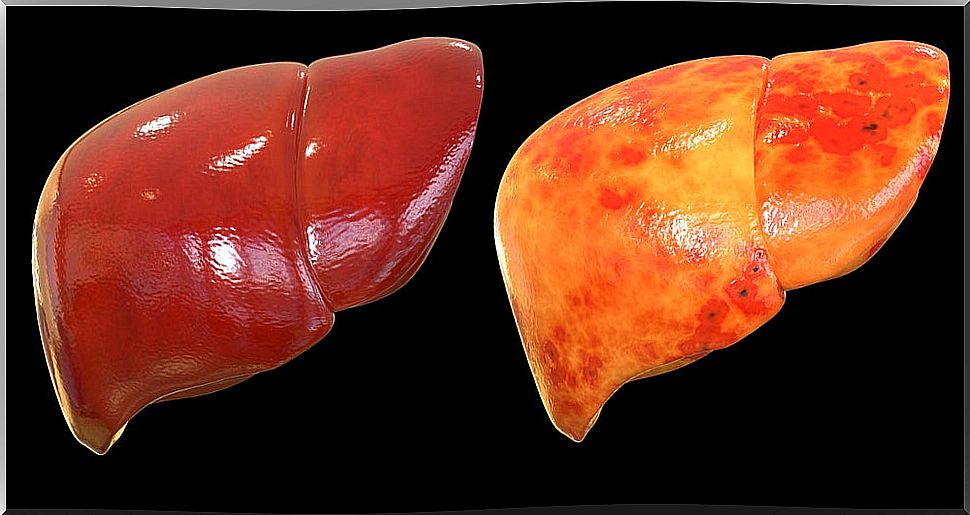
Treatment Of Hepatic Steatosis
The treatment of fatty liver or fatty liver will depend on the causes that have triggered it.
There are no drugs that by themselves fight this disease. However, the reabsorption of fat from the liver is possible, which will lead to healing.
It can be achieved by adopting habits of a healthy lifestyle:
- Change harmful habits for healthy ones.
- Avoid risk factors as well as their triggers.
- Carry out the correct treatment of the disease.
There are different situations in which a patient can suffer from fatty liver. For each one, the treatment will be different, since it depends on the cause:
- Hepatic alcohol steatosis.
- Fatty liver in an obese patient.
- Fatty liver in diabetic person.
Treatment of alcoholic fatty liver disease

In this type of steatosis, the treatment will be mainly the reduction of alcohol consumption to a minimum or its complete elimination.
It has been scientifically proven that liver fat begins to disappear within 3 to 4 weeks after quitting alcohol consumption.
Treatment of fatty liver due to obesity or diabetes
In these cases, the treatment will be aimed at correcting the alterations of the disease that contribute to the development of steatosis. This is the case, for example, of insulin resistance.
The main recommendation for obese people are healthier lifestyle habits. They must maintain a diet balanced and low – calorie and perform physical exercise at the least 3 times a week for 30 minutes. In this way, you will achieve the ideal weight gradually.
It will try to avoid the yo-yo effect. The mobilization of fatty acids from adipose tissue to the liver would deprive it of the supply of other necessary nutrients. Consequently, steatosis would worsen and existing tissue lesions would worsen. Therefore, weight loss must be gradual and progressive.
There is also a pharmacological treatment for cases in which the disease continues to worsen.
Pharmacotherapy
At present, the treatment of hepatic steatosis is mainly based on drugs. Among the most used drugs are:
- Drugs that increase insulin sensitivity :
- Metformin.
- Rosiglitazone.
- Pioglitazone.
- Antioxidant drugs:
- Vitamin E.
- Drugs that promote weight loss:
- Orlistat.
- Rimonabant.
- Other types of drugs:
- Silymarin.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid.
Metformin
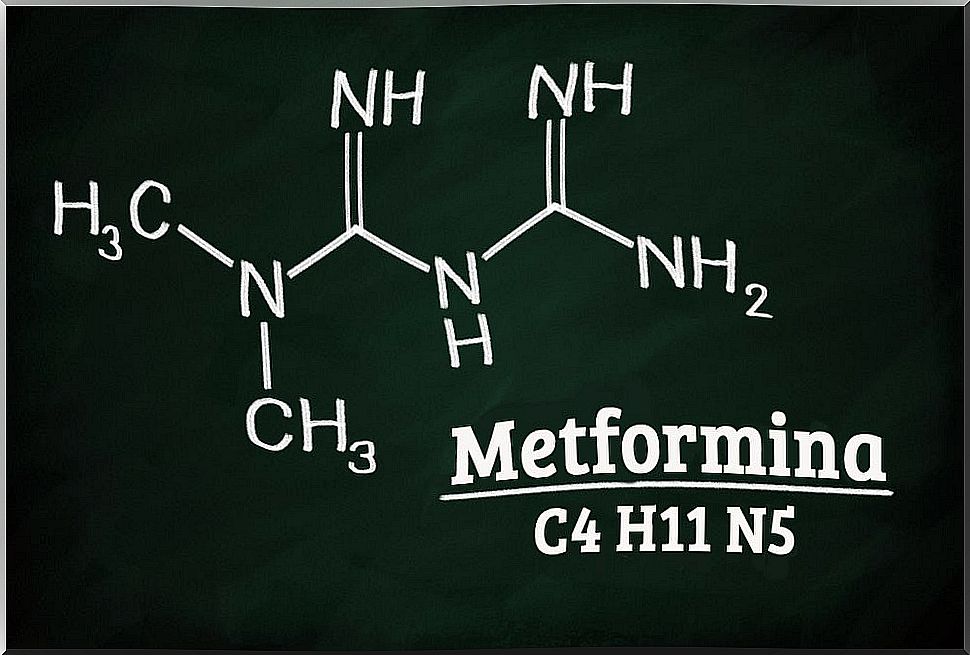
The mechanism of action of this drug is not very well understood. Despite this, its pharmacological action improves insulin sensitivity in adipose and muscle tissue.
Thus, it improves the biochemistry of the liver and the degree of steatosis, without significant effects on inflammation and liver fibrosis. In addition, it has a good safety profile.
Currently, studies are continuing in patients treated with this drug to investigate other possible benefits.
Rosiglitazone and Pioglitazone
These two drugs activate the PPAR-gamma protein, a protein in the cell nucleus responsible for increasing the peripheral utilization of glucose.
Treatment of hepatic steatosis with these two drugs leads to a significant improvement in liver tissue and biochemistry, especially in non-diabetic patients.
Orlistat and Rimonabant
Orlistat is a gastric and pancreatic lipase inhibitor that has some efficacy in improving the degree of steatosis and histological activity.
Today they are not widely used as clinical trials are still being conducted to determine their efficacy and safety.
Silymarin
It is a hepatoprotective compound. On the one hand, it captures free radicals and, on the other, it is an antioxidant and inhibits lipid peroxidation.
Silymarin is also a liver regenerator that increases protein synthesis in liver cells (hepatocytes), stimulates DNA polymerase, and increases rRNA synthesis.
This drug can produce some adverse reactions, although they are of low frequency. These reactions include: gastralgias, allergic reactions and diarrhea.
Other types of treatment
In addition to drug treatment, surgical treatment is also possible. It consists of a liver transplant. However, it is possible only in cases of advanced cirrhosis.
The results of surgery are generally good. However, it is possible that new histological lesions typical of steatosis may appear in the graft.









