Mistletoe: Benefits And Precautions
Mistletoe is a medicinal plant that has been used to stimulate the immune system, reduce anxiety, and improve cardiovascular health. How is it used? Find out!
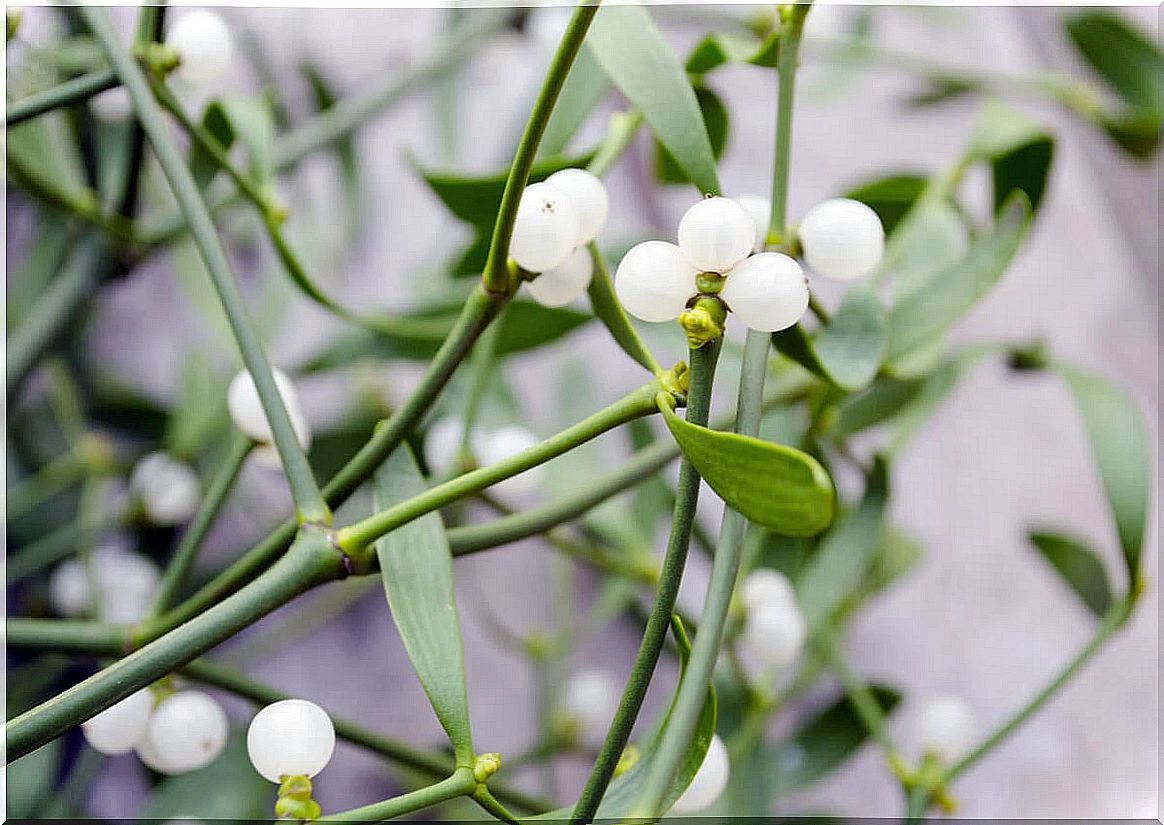

The mistletoe, whose scientific name is Viscum album, is a plant with berries, leaves and stems that are used for medicinal purposes. Although there are an estimated 1,300 species, the European mistletoe is the most common when it comes to improving health.
According to a publication in the pharmaceutical encyclopedia Drugs , it is a hemiparasitic species that grows on host trees such as oak, birch and apple. This means that, although the photosynthesis of the mistletoe is independent, it obtains water and nutrients from its host.
Now, since ancient times it has also been part of ceremonies and legends. Not only is it a symbol of the winter season, but it was used in fertility rituals and as therapy against diseases. What does science say about its benefits? We’ll tell you then.
Health benefits of mistletoe
An article published through the Archives of Pharmacal Research medical journal states that mistletoe has been studied for its medicinal composition. It, which includes substances such as lectins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, sterols, lignans, terpenoids, alkaloids and fatty acids, among others, gives it the following properties:
- Immunomodulator.
- Hepatoprotective.
- Neuroprotective.
- Antimicrobial.
- Antifungal.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Cardiac protector.
- Antidiabetic
However, despite the research, for now there is not enough evidence to affirm its efficacy and safety. Anyway, the aforementioned study concludes that, in the future, mistletoe may be the basis for new complementary therapies to support the treatment of various diseases. What benefits are attributed to it?

Mental health
Herbal remedies are not a first-line treatment when it comes to addressing mental health problems. Even so, in some cases they are considered an adjunct to improve states of anxiety, stress and insomnia. Regarding this, a study published in Integrative Cancer Therapies made some findings.
In research, European mistletoe extracts were helpful in reducing feelings of fatigue, exhaustion, depression, and anxiety in cancer patients. This is because the chemical compounds in the herb stimulate the release of neurotransmitters that calm the nervous system.
Cancer
Of all the plants associated with positive anticancer effects, mistletoe has been one of the most researched. Entities such as the National Cancer Institute state that the extracts of this plant are one of the complementary therapies with more evidence regarding its anticancer effects.
The findings suggest that mistletoe has components that help inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells. It even seems that in some cases it helps to eliminate existing malignant cells.
Meta-analysis, such as one reported in BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies , conclude that the plant improves the quality of life of patients with this disease. In particular, there are mental health benefits and symptoms such as nausea and pain are reduced.
Meanwhile, previous research has also determined that the plant has the potential to improve blood counts and shrink tumors. Still, the National Cancer Institute states that more clinical trials are needed. In addition, it clarifies that it is not yet approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Immune system
Linked to the previous benefit, it should be noted that mistletoe has been valued for its immunomodulatory capacity. Several studies, such as one reported in Phytotherapy Research , found that European mistletoe improves the immune response in cancer patients. Furthermore, it was a well tolerated treatment in the trial.
Although much of the research has focused on its immunomodulatory effect against cancer, anecdotal data show that it also increases defenses in healthy adults. This reduces the risk of common viral infections, such as colds and flu.
Diabetes
In traditional medicine, mistletoe and its extracts are used as adjuvants to regulate blood glucose levels. On this, an investigation published in the Journal of Endocrinology determined that the plant has compounds that stimulate the secretion of insulin in pancreatic cells. For this reason, it is considered antidiabetic.
Inflammation
A number of diseases are associated with alterations in inflammatory processes in the body. Mistletoe, according to popular literature, has the ability to reduce inflammation. While more clinical trials are needed, there is scientific evidence to support these properties.
A study in the Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research concludes that the plant has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential. He even suggests investigating it as a possible candidate against diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Meanwhile, a publication in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine suggests that mistletoe extracts relax the vascular and intestinal muscle, which favors the relief of gastrointestinal problems associated with inflammation, such as spasms.
Mistletoe side effects and precautions
For most healthy adults, moderate mistletoe use is not a problem. Some side effects include headaches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, low blood pressure, and dizziness. However, these are usually caused by an excessive intake of the plant.
Injectable mistletoe tests on cancer patients have found it to cause pain and swelling at the injection site. However, it is an unapproved treatment and, therefore, it is probably not among the therapeutic options.
The plant is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Patients with primary or secondary brain tumors.
- Patients with leukemia or malignant lymphoma.
- People who are taking anticoagulants, antidepressants, medications for heart disease or high blood pressure.

How to consume mistletoe?
Keep in mind that most mistletoe research has been done from intravenous presentations. However, this has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and therefore should not be on the market.
Now, it is possible to find mistletoe in the form of liquid extract, dried herb or tea bags. Although it is unknown if they are effective, there are those who choose to use it in these ways. If so, it is not advisable to take more than 10 grams a day.
Mistletoe tea
- Add a teaspoon of dried mistletoe leaves (5 grams) to a cup of boiling water (250 milliliters).
- Let the drink rest for 10 minutes, strain and consume.
- You can take it 2 times a day.
Mistletoe: a supplement for health
Scientific studies on mistletoe have determined its potential to improve health. However, its level of safety and efficacy needs to be investigated further to make claims. Therefore, it is not yet an FDA approved treatment and it is not a first-line option.
It is important to use the plant in moderation, without exceeding the recommended daily dose (10 grams). In addition, you have to be careful in case of having a disease or being under medical treatment. It should not be ignored that there is a risk of interactions and side effects.